For anyone starting on the rewarding journey into computer networking, Packet Tracer is an indispensable learning tool.
If you’re planning to take the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) ) exam, you must practice on the Packet Tracer networking simulation software from Cisco.
Download Packet Tracer
On Cisco’s Networking Academy web site, the latest 64-bit version of Packet Tracer is available for both Linux and Windows for free.
So I headed to Cisco’s Packet Tracer Download web site and downloaded the Packet Tracer 7.2.1 tarball for Linux.
Before you can download Packet Tracer, you must register with the site.
For the purpose of this post, I downloaded Packet Tracer 7.2 to a 10-year-old Dell 780 desktop PC running Linux Mint 18.3.
(By the way, I tried the Windows version of Packet Tracer too and got it to work without sweat. Since my Windows 10 laptop is an anemic device with just 4GB RAM, I prefer to run Packet Tracer on my Linux PC, which has a more generous 8GB RAM.)
Extracting the File
I extracted Packet Tracer 7.2.1 into the same folder in which I had downloaded the file.
Now that you have downloaded the Packet Tracer software, fire up your terminal and extract the software (see command below).
mike@familypc ~/Downloads/Packet-Tracer $ tar -xvzf Packet-Tracer-7.2.1-for-Linux-64-bit.tar.gz art/ art/IoE/ art/IoE/Sensors/ art/IoE/Sensors/MotionSensor.png art/IoE/Sensors/GenericSensor.png [output truncated] templates/Smart LED.ptd tpl.linguist tpl.packettracer mike@familypc ~/Downloads/Packet-Tracer
Now that we completed the extraction, let’s take a quick look at the folder.
mike@familypc ~/Downloads/Packet-Tracer $ ll -a total 305296 drwxrwxr-x 11 mike mike 4096 Mar 29 20:11 ./ drwxr-xr-x 18 mike mike 4096 Mar 24 16:19 ../ -rw-rw-r-- 1 mike mike 710787 Mar 26 22:19 1.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Help and Navigation Tips.pdf drwxrwxr-x 24 mike mike 4096 Dec 9 23:45 art/ drwxrwxr-x 6 mike mike 4096 Dec 9 23:45 backgrounds/ drwxr-xr-x 8 mike mike 4096 Dec 7 15:41 bin/ -rw-rw-r-- 1 mike mike 172942 Mar 17 17:31 Cisco Packet Tracer FAQs.pdf -rwxrwxr-x 1 mike mike 14510 Dec 14 20:23 eula721.txt* drwxr-xr-x 15 mike mike 4096 Dec 10 18:44 extensions/ drwxr-xr-x 3 mike mike 4096 Dec 7 15:27 help/ -rwxr-xr-x 1 mike mike 4134 Dec 14 19:56 install* drwxrwxr-x 2 mike mike 4096 Dec 9 23:45 languages/ -rw-rw-r-- 1 mike mike 311645539 Mar 17 17:31 Packet-Tracer-7.2.1-for-Linux-64-bit.tar.gz dr-xr-xr-x 21 mike mike 4096 Dec 9 23:45 saves/ -rw-r--r-- 1 mike mike 1237 Dec 9 23:45 set_ptenv.sh -rw-r--r-- 1 mike mike 1207 Dec 9 23:45 set_qtenv.sh drwxrwxr-x 2 mike mike 4096 Dec 9 23:45 Sounds/ drwxrwxr-x 3 mike mike 4096 Dec 9 23:45 templates/ -rw-r--r-- 1 mike mike 159 Mar 5 2018 tpl.linguist -rw-r--r-- 1 mike mike 177 Dec 7 15:40 tpl.packettracer mike@familypc ~/Downloads/Packet-Tracer $
Everything looks good.
So let’s move to the next step: Running the install script.
Installing Packet Tracer
I did not encounter any major issues in installing Packet Tracer except for a minor bump when the process stopped momentarily and asked for my sudo password to copy the files into opt/pt.
mike@familypc ~/Downloads/Packet-Tracer $ ./install
Welcome to Cisco Packet Tracer 7.2.1 Installation
Read the following End User License Agreement "EULA" carefully. You must accept the terms of this EULA to install and use Cisco Packet Tracer.
Press the Enter key to read the EULA.
Cisco Packet Tracer
Software License Agreement
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ THIS CISCO PACKET TRACER SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT (THE "AGREEMENT") CAREFULLY. DOWNLOADING, INSTALLING OR USING THE CISCO PACKET TRACER SOFTWARE CONSTITUTES ACCEPTANCE OF T
HIS AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO ALL OF THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, THEN CISCO SYSTEMS, INC. ("CISCO") IS UNWILLING TO LICENSE THE SOFTWARE TO YOU AND YOU ARE NOT AUTHORIZED TO DOWNLOAD, INST
ALL OR USE THE SOFTWARE.
I. DISTRIBUTION RIGHTS. The terms in this Section I (Distribution Rights) of the Agreement apply solely to any Cisco Networking Academy instructor, administrator or other person or entity approved in writing by Cisco Systems, Inc. (each, an "Instructor") to distribute and use the Cisco Packet Tracer software and related documentation (collectively, the "Software") in accordance with the terms and conditions of this Agreement.
[output truncated]
Cisco, Cisco Systems, and the Cisco Systems logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. in the U.S. and certain other countries. Any other trademarks mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
Do you accept the terms of the EULA? (Y)es/(N)o
yes
You have accepted the terms to the EULA. Congratulations. Packet Tracer will now be installed.
Enter location to install Cisco Packet Tracer or press enter for default [/opt/pt]:
Installing into /opt/pt
Not able to create and copy files to /opt/pt
Should we try to gain root access with sudo? [Yn] y
[sudo] password for mike:
Installing into /opt/pt
Copied all files successfully to /opt/pt
Should we create a symbolic link "packettracer" in /usr/local/bin for easy Cisco Packet Tracer startup? [Yn] y
Type "packettracer" in a terminal to start Cisco Packet Tracer
Writing PT7HOME environment variable to /etc/profile
Writing QT_DEVICE_PIXEL_RATIO environment variable to /etc/profile
Cisco Packet Tracer 7.2.1 installed successfully
Please restart you computer for the Packet Tracer settings to take effect
Voila, Packet Tracer 7.2 is now installed on my Linux Mint PC.
After rebooting the system, I was able to launch Packet Tracer and get it to work without any issues.
To launch Packet Tracer, head to the terminal and just issue the command packettracer:
mike@familypc ~ $ packettracer Starting Packet Tracer 7.2.1
But if you’re like me and want to do more with less, you can set up an alias by opening the .bashrc file with nano or vim and inserting alias pt=”packettracer” at the end of the file, save and close it. Don’t forget to run source ~/.bashrc so that you don’t have to close the terminal for the new alias to work. The next time you want to launch Packet Tracer, just type pt instead of the longer packettracer on the terminal.
Overall, I did not encounter any showstoppers in the process of downloading, installing or using Packet Tracer 7.2.1 on my Linux PC.
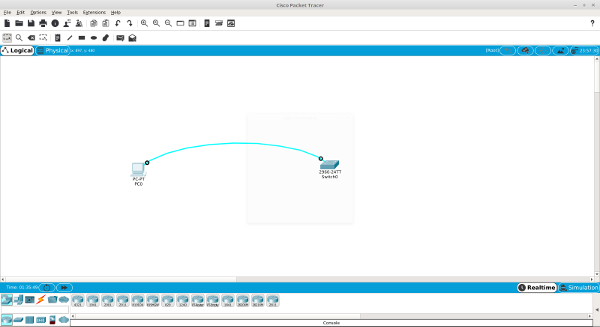
As you can see from the Packet Tracer image at the top of this post, I even moved a PC and switch into the logical work area and hooked them up with a console/rollover cable.
Getting Packet Tracer 7.2 on my Linux desktop PC took about five-minutes.
Since Linux Mint is based on Ubuntu, Packet Tracer should work on Ubuntu too.
One of these days, I’ll test Packet Tracer on my CentOS 7 desktop and see how the process goes.

 Create E-Mail Account in Plesk
Create E-Mail Account in Plesk